Main navigation
Anatomic Pathology supports service, teaching and research activities. Descriptions of each of the areas and their contributions to our missions are listed below.
The section of Anatomic Pathology (AP) is composed of:
Anatomic Pathology Records
Anatomic Pathology Records assists with report preparation, transcription, distribution and filing of final Surgical Pathology and Autopsy reports.
This area provides custodial oversight for all archived tissue slides and fields requests for materials and information (pathology slides and reports) from both patients and physicians. AP Records is also responsible for the coordination of pathology materials for intra- and inter-departmental conferences.


Decedent Care Center (Autopsy Services)
The Decedent Care Center (DCC) provides compassionate and professional support to families and hospital staff following the death of a patient.
The DCC serves to facilitate family visits, organ/tissue donation, and the release of decedents to funeral homes. The autopsy service strives to sustain a clinical goal of patient-centered medicine for the benefit of families and hospital staff alike.
Cytopathology Laboratory
Cytopathology is a multifaceted laboratory performing service, education and scholarly work.
The service area of the laboratory is responsible for preparation, staining and microscopic examination of patient samples. The cytologic samples may be used for screening (cervical-vaginal), a diagnosis (FNA), or (when a cytology is performed in conjunction with a surgical procedure) improving the overall diagnostic accuracy (brushes, washes).
Cytology also has a pathologist-based Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) service located in the Clinical Cancer Center for palpable masses. The pathologists also travel to other clinic areas for FNA of non-palpable thoracic, abdominal and soft tissue masses.
Fellowship program
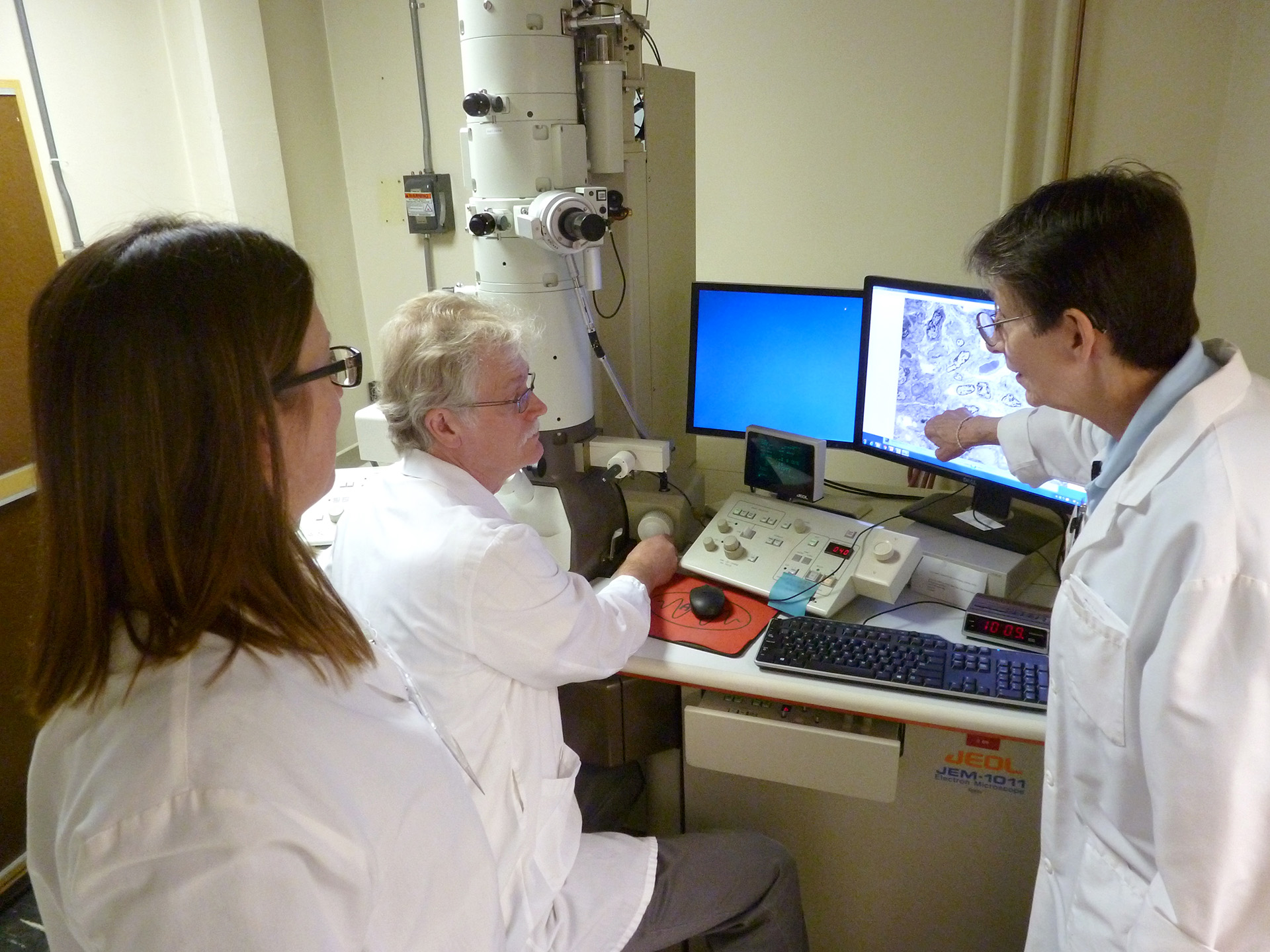


Electron Microscopy Laboratory
The electron microscope is a tool that projects electrons through extremely thin tissue sections to produce a two-dimensional image on the screen or photograph.
Tissue specimens from kidney, brain muscle and nerves are fixed, embedded, sectioned, and photographed at the cellular level for diagnostic evaluation.
The Diagnostic Electron Microscopy Laboratory has evolved from an emphasis in the beginning on tumor differentiation to the current emphasis on ultrastructural studies of renal and neurology specimens. The laboratory also supports a fair amount of departmental research. The laboratory is located in the basement of the Medical Research Center and is equipped with a JEOL 1011 Transmission Electron Microscopy, and Reichert-Jung Ultracut E ultramicrotomes.
Histopathology Laboratory
The Histopathology Laboratory offers a comprehensive program of histology services. The laboratory provides routine surgical tissue processing, embedding, microtomy, and cytochemical staining in preparation for review by house staff and faculty pathologists. The laboratory also offer neurohistologistic support for muscle, nerve, and brain specimens including a variety of enzyme histochemical studies for the evaluation of myopathic and neurogenic disorders.


Immunopathology Laboratory
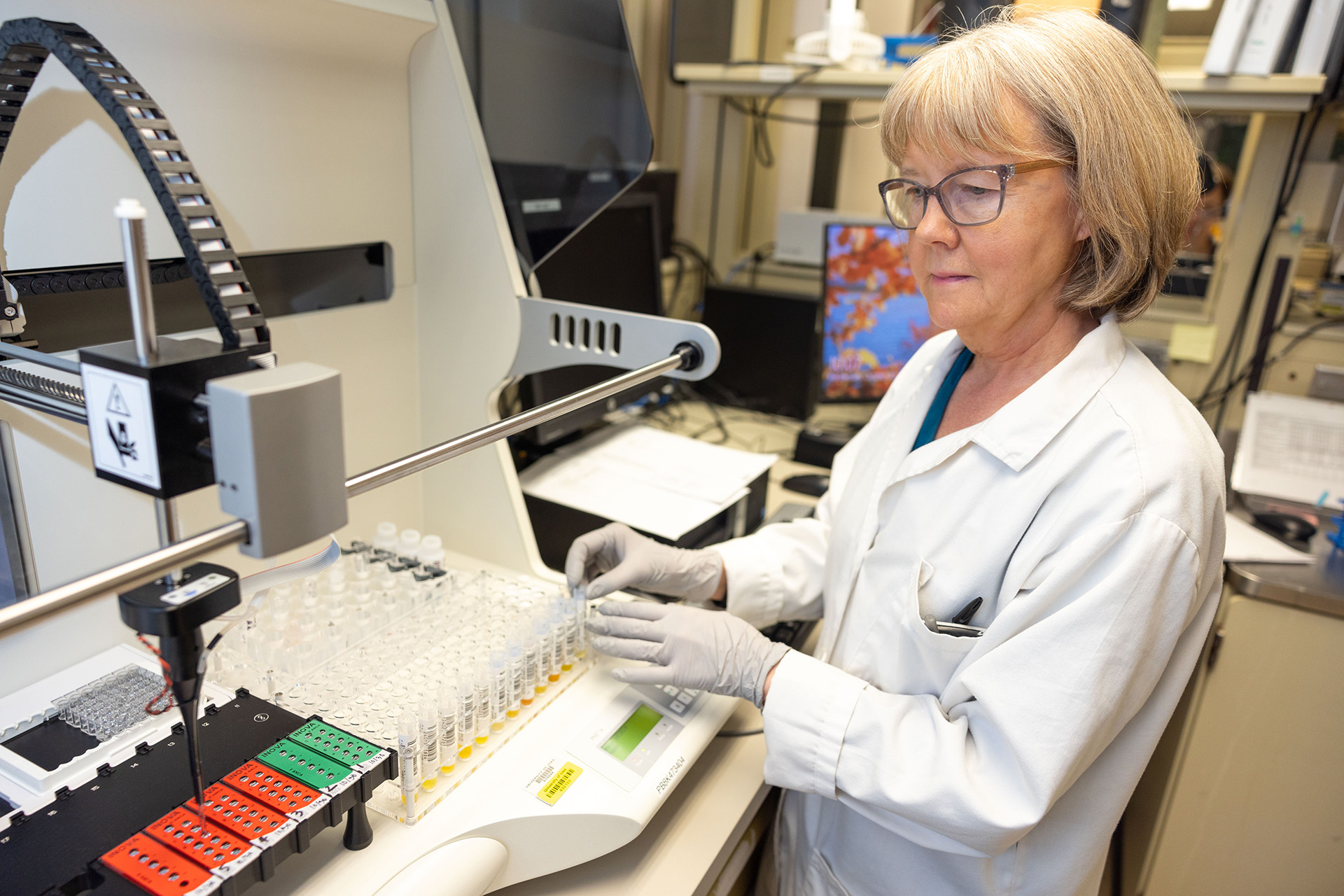
The Immunopathology Laboratory performs several categories of diagnostic testing including autoimmune disease serologies, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence microscopy, immunofixation and high-resolution agarose electrophoresis.
Autoimmune disease serologies include screening for diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome, scleroderma, Wegner's granulomatosis and related vasculitides, autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease and others. Testing methodologies used include enzyme immunoassay, indirect immunofluorescence microscopy, and immunodiffusion.
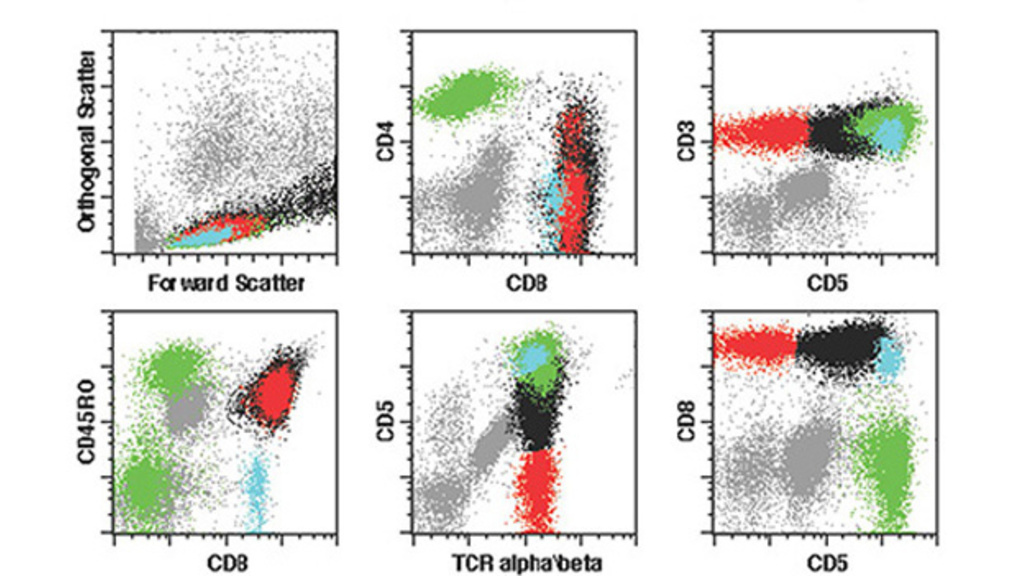
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is done on bone marrow, peripheral blood, fine needle aspirations, miscellaneous body fluids, lymph nodes and tumors. Flow cytometry has a wide range of uses from typing lymphomas and leukemias to quantitation of lymphocyte subsets in suspected immunodeficiency diseases.

Immunohistochemistry staining
Immunohistochemistry staining is done primarily on formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissues using automated staining equipment. A large number of antibodies are available to immunophenotype and identify the source of tumors and to detect certain infectious agents (particularly viruses) in tissue sections. In-situ hybridization studies are also performed to identify certain types on infections, particularly Epstein-Barr virus.

Immunofluorescence microscopy
Immunofluorescence microscopy is done on frozen sections of skin, kidney, lymph node, and tumors. It is used both to diagnose autoimmune diseases of the skin, mucosae and the kidney and to immunophenotype lymphoid proliferations and several other types of tumors.
Surgical Pathology and Fellowship Program
The Surgical Pathology Laboratory receives all biopsy and surgical resection specimens obtained from patients seen at University of Iowa Health Care as well as specimens referred to University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories by outside institutions.
During the pre-analytical process the laboratory will accession each specimen with a unique case and part identification and then label these specimens and their corresponding tissue cassettes for subsequent analysis. Faculty and staff members working under the direction of the medical director then perform and record a gross description of the specimen including dissection and sampling for histologic evaluation. Providers within this laboratory also perform intraoperative pathology consultations to aid and support the decision-making process as patients are undergoing surgery.
After processing and tissue slide staining by the Histology Laboratory, a Surgical Pathology fellow examines and records a preliminary diagnosis in the laboratory information system. Surgical pathology residents and externs then perform a full microscopic examination and draft a description and diagnosis. The histology slides and dictated reports are then reviewed with a faculty pathologist who revises and/or amends the report as necessary in preparation for release of a final report to the ordering provider.
Fellowship program
Learn more about our Surgical Pathology Fellowship.

